Scientists reveal: What did the ancient human "Mengzi people" look like 14,000 years ago?
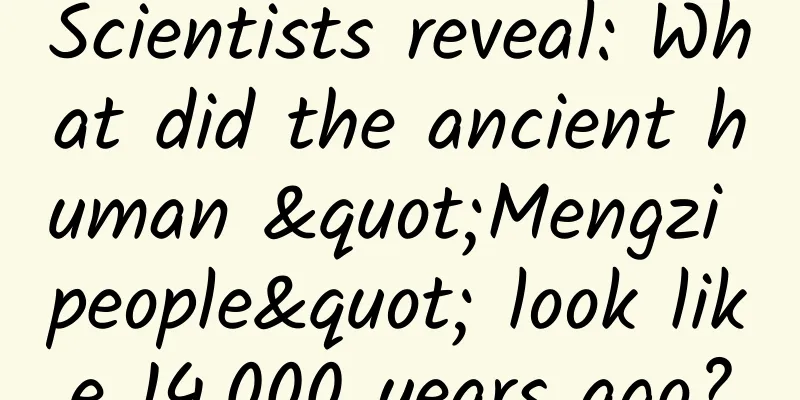
|
Xinhua News Agency, Kunming, July 15 (Reporter Yue Ranran) Through ancient DNA research, Chinese scientists have unveiled the mystery of the "Mengzi people" who lived 14,000 years ago. The results were published online on the 14th in the internationally renowned academic journal "Contemporary Biology". The "Mengzi Man" was unearthed in 1989 in Malu Cave, located in Mengzi City, Honghe Hani and Yi Autonomous Prefecture, Yunnan Province. Experts have identified the cave as an ancient human site. After rescue excavations, more than 30 ancient human fossils, including the skull, mandible, and femur of the "Mengzi Man", as well as animal fossils such as red deer, macaques, and black bears were unearthed in the cave. Maludong site. (Provided by Yunnan Provincial Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology) Zhang Xiaoming, the first author of the paper and a researcher at the Kunming Institute of Zoology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, said that the results of physical anthropological research on a relatively complete skull found in Malu Cave showed that the owner of the skull was a young woman, with a height and weight of about 155 cm and 46 kg respectively, a low skull height, dark skin, a low nose bridge, a small brain capacity, and a hunting and gathering life about 14,000 years ago. "Although the 'Mengzi people' are within the variation range of modern humans, their morphological characteristics are very complex," said Zhang Xiaoming. The skull of the "Mengzi Man". (Photo provided by the Mengzi Cultural Relics Management Office) In order to uncover the mystery of the "Mengzi people", researchers used skull fragments of the "Mengzi people" to conduct ancient DNA genetics analysis and found that the "Mengzi people" were early modern humans, not ancient humans. The study also found that from Malu Cave in Yunnan in the south to the Heilongjiang River Basin in the north, the genetic components shared by the Chinese population had been formed about 16,000 to 14,000 years ago, providing clues for the Chinese civilization exploration project. In addition, by constructing the genetic model of the skin color of the "Mengzi people", the researchers speculated that the "Mengzi people" may have dark skin, and that the genetic mutation of the "light skin color" of the Chinese population may have occurred as early as about 7,500 years ago in the southeastern coastal areas of my country, which also makes the Chinese population "whiter" than the Southeast Asian population. Source: Xinhuanet |
<<: Beware! Bacteria "Killers" in the Refrigerator
>>: Go to 331 and cross the northern border of China!
Recommend
If this kind of sound appears in the ears, does it mean that you are not far from becoming deaf?
Reviewer of this article: Chen Haixu, Deputy Dire...
Angry Birds announces phasing out Windows Phone: no more updates
Windows Phone, Android and iOS are generally recog...
Xpeng Motors updates its prospectus with a valuation of approximately US$8.6 billion
As new energy vehicles become increasingly popula...
By reading "The Art of War", let's talk about how to promote and operate APP?
I have recently been studying " The Art of W...
26 satellites in one rocket! Lijian-1 Yao-2 carrier rocket successfully launched
At 12:10 Beijing time on June 7, 2023, the Lijian...
The Jing River and the Wei River are clearly separated, which one is clear?
From today's aerial photos, we can see that t...
Confession of the first-class protected animal "Six-Unlike" Takin: We are cute and gentle, but...
Expert: Guo Geng, Researcher, Beijing Biodiversit...
The pitfalls of iOS App background tasks
Most iOS apps will encapsulate some key tasks int...
World Hypertension Day丨Take this anti-stress manual and stay away from the "invisible killer"
Hypertension is a common chronic disease, known a...
3D parallax guide page
Source code introduction: 3D parallax guide page,...
Cardiologists remind: These symptoms are signs of blood vessel blockage and thrombosis! This is how to prevent
Vascular blockage is a very serious disease. Some...
Tik Tok operation and promotion plan, super detailed!
Recently, Douyin released the "2020 Spring F...
Big data tells you what the elderly are busy with when they go online?
This era does not only belong to young people. In...
In-depth analysis | How did the 400 million yuan worth of advertising and content of "The Debaters" come together so perfectly?
There is a variety show that inserts advertisemen...
Does liver cancer come quietly? Why is early liver cancer painless? Read more →
Currently, liver cancer ranks fourth in incidence...









